Introduction
October marks Cybersecurity Awareness Month, a crucial time to reinforce our knowledge and habits around digital safety. Organized by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Cybersecurity Alliance, this month-long initiative, themed “Secure Our World,” aims to help individuals and organizations strengthen their defenses against the growing threat landscape. With scams becoming increasingly sophisticated, it’s essential to take proactive measures to protect your information and devices.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Common Cyber Threats
- Essential Cybersecurity Practices for Individuals
- Protecting Your Devices and Networks
- Staying Safe from Scams
- Cybersecurity Best Practices for Businesses
- What to Do If You Fall Victim to a Scam
- FAQs About Cybersecurity
1. Understanding Common Cyber Threats
To effectively protect yourself, it’s vital to recognize the most common cyber threats:
- Phishing Attacks: Fraudulent messages designed to trick you into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials or credit card details.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts your data and demands a ransom for access.
- Social Engineering: Manipulative tactics that exploit human psychology to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Smishing (SMS Phishing): Scams sent via text messages urging recipients to click malicious links.
By understanding these threats, you can recognize early warning signs and take appropriate action.
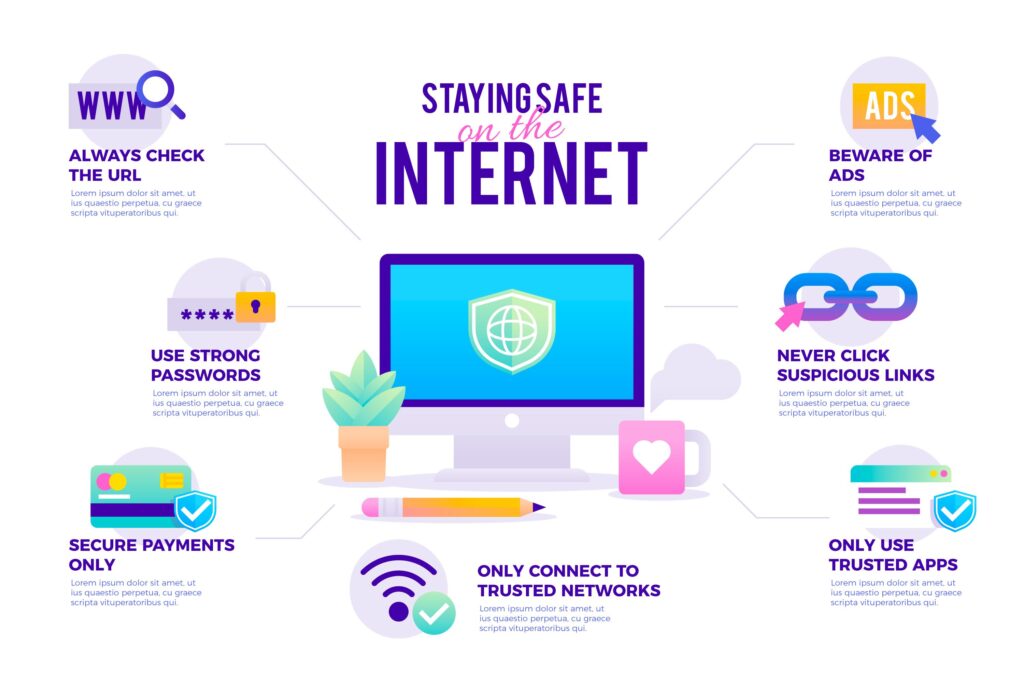
2. Essential Cybersecurity Practices for Individuals
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Avoid reusing passwords across different accounts. Utilize a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second verification method beyond just a password.
- Regularly Update Software: Ensure your devices and applications are always up-to-date to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Back Up Important Data: Regularly back up your data to an external drive or cloud service to prevent loss during cyber incidents.
3. Protecting Your Devices and Networks
- Secure Your Home Network: Use a strong, unique Wi-Fi password and consider hiding your network’s SSID (name) to minimize unauthorized access.
- Install Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Regularly scan your devices to detect and remove threats.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): Protect your online activity, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks, by encrypting your internet connection.
4. Staying Safe from Scams
- Verify the Source: If you receive a suspicious email or message, contact the organization directly through an official channel rather than clicking on links.
- Be Cautious of Unsolicited Requests: Scammers often use urgency, like a “security alert,” to prompt immediate action.
- Monitor Financial Accounts Regularly: Check bank statements and credit reports for any unusual activity to catch fraud early.
5. Cybersecurity Best Practices for Businesses
Businesses must prioritize cybersecurity, particularly during October, by:
- Conducting Employee Training: Educate employees on recognizing phishing attempts and secure online behaviors.
- Implementing Access Controls: Limit access to sensitive data based on job roles to reduce the risk of insider threats.
- Setting Up Regular Security Audits: Regularly review and update security policies to address evolving threats.
- Engaging in Phishing Simulations: Test employees with simulated phishing emails to reinforce training.
6. What to Do If You Fall Victim to a Scam
- Stop All Communication: Cease contact with the scammer immediately to prevent further compromise.
- Change Your Passwords: Update credentials for all potentially affected accounts.
- Report the Incident: File a complaint with the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) or the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and notify your bank or credit card company if financial information was compromised.
7. FAQs About Cybersecurity
- What is the most effective way to prevent phishing? Multi-factor authentication and cautious email habits are the best defenses against phishing attacks.
- How often should I update my passwords? It’s recommended to update passwords every three to six months, especially for high-value accounts like banking or email.
- Are password managers safe? Yes, most reputable password managers offer secure, encrypted storage for managing and generating strong passwords.
Conclusion
By following these practices and staying vigilant, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyber threats. Remember, cybersecurity is a shared responsibility—staying informed and proactive is key to protecting yourself and others online.
